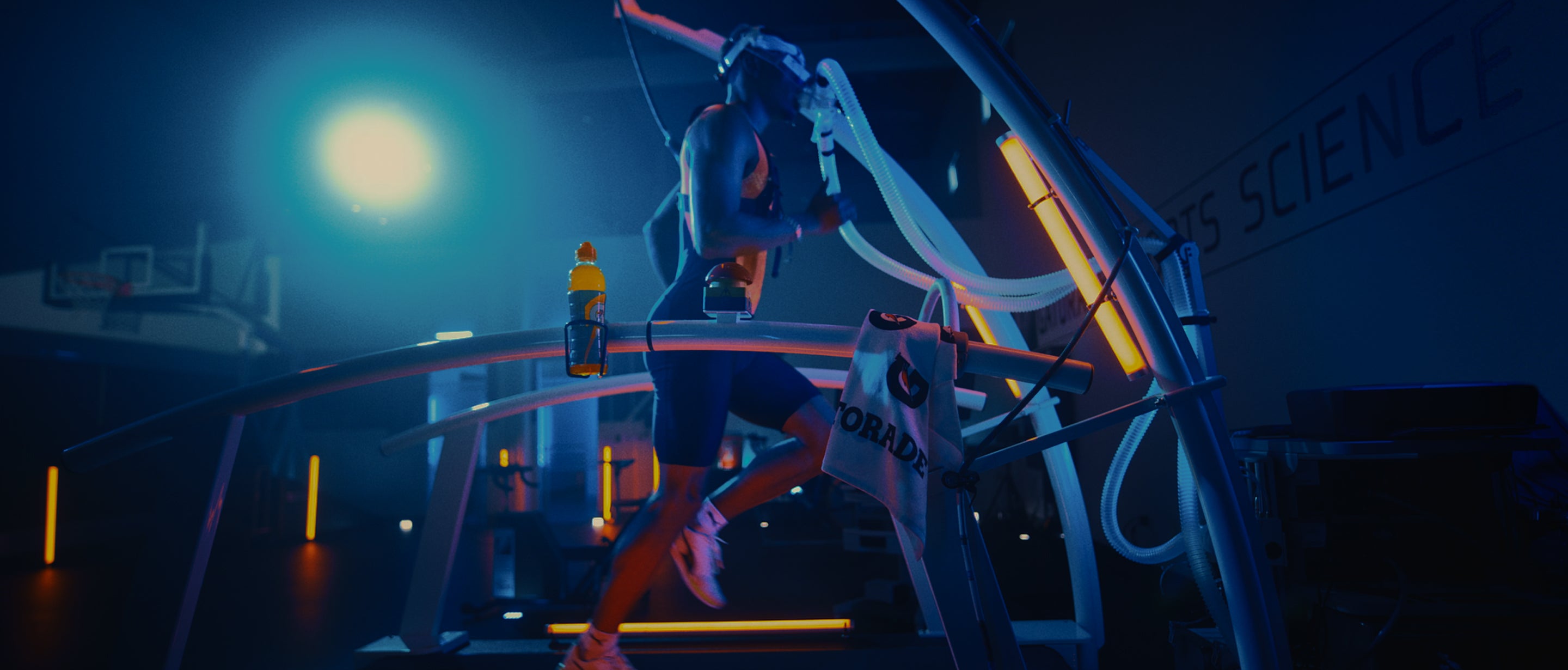
1. Rehydrate
Consuming fluids during exercise keeps your blood volume up and your core temperature down. Both help you fight fatigue so you can continue to perform at your best.

2. Replenish
When you sweat you lose more than just water, you also lose electrolytes. Electrolytes like sodium and potassium play a key role in brain-to-muscle communication, which is important for performance. Intense physical activity may lead to intense sweating, and you have a lot to lose during a game or practice. The average hockey player loses 1.5L of sweat per hour, and in certain cases sweat loss can account for more than half your entire recommended daily intake of sodium.

3. Refuel
Carbs are the preferred fuel source for your brain and muscles. During training, you may use or deplete carbohydrate energy stored in the form of glycogen which can negatively affect performance. Your body breaks down carbohydrates into sugar molecules. For your brain, sugar can help improve concentration, helping you make better split-second decisions during the game. For your muscles, sugar is easily digested, absorbed and quickly oxidized to provide energy during high-intensity or prolonged exercise.